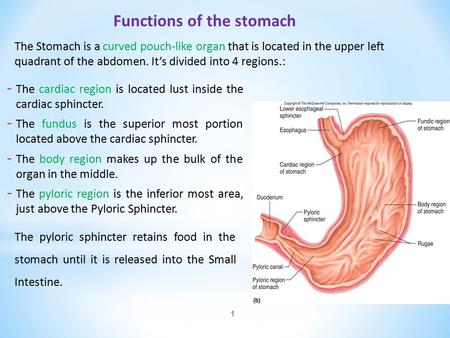
Describe the Function of the Stomach
It secretes gastric juice which is extremely acidic in nature and this really helps in making life easier for the other parts of the digestive system. Thus the stomach holds food and parses only small amounts into the small intestine at a time.
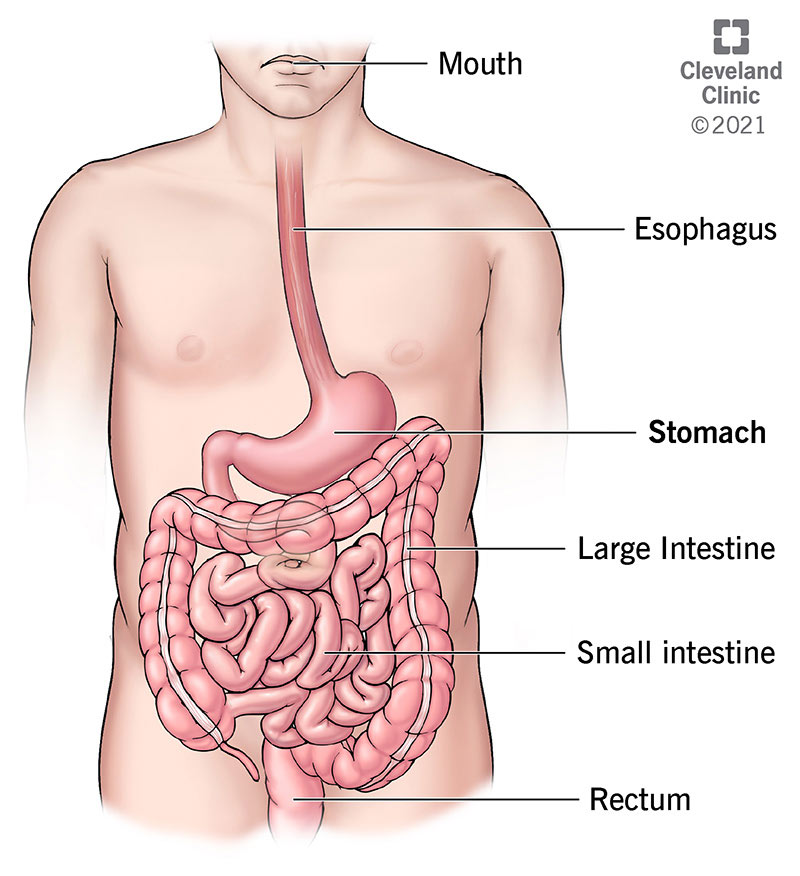
Stomach Anatomy Function Diagram Parts Of Structure
The stomach is the most dilated part of the digestive system lying between the esophagus and duodenum.

. - distention of stomach activates vagus parasympathetic-amino acids and peptides in stomach stimulate G cells - enteric NS causes muscle contractions 3. The churning action of the stomach muscles physically breaks down the food. What are the stomach main functions.
B 1 111 TIL T T. The stomach is a sack-like muscle organ positioned directly below the liver on the upper-left side of the abdomen. T O Words 3.
The stomach can sense independently to the tongue and oral taste receptors glucose carbohydrates proteins fats and sodium glutamate via the vagus nerve which allows the brain to link the nutritional value of foods to their tastes. It also helps to heal itself and the stomach if the first layer of the mucosal lining is breached. The major function of the stomach is to digest food.
Enteric NS and gastrin cause strong SM contractions. The stomach secretes acid and enzymes that digest food. The reservoir capacity of the stomach allows it to increase its volume significantly while internal pressure increases only slightly.
Food storage Acidic breakdown of swallowed food Sends mixture on to the next phase in the small intestine. What is the mesentery. And it even prevents disease by encasing bacterial and viral threats before they can multiply.
The functions of a stomach is to hold digest process and release food for digestion as it empties into the small intestine. The stomach acids and enzymes work to break down food which is then released into the small intestine. The stomach functions to initiate the digestive process and to deliver ingested nutrients via a rhythmic motion to the small intestine.
You can ingest. Distension of stomach stimulates vagus parietal and G cells Presence of AApeptides stimulates G cells. Function of the stomach.
It accomplishes this by secreting stomach acid and enzymes to digest food and churning the food by the periodic contraction of the stomach muscles. The stomach releases acids and enzymes for the chemical breakdown of food. Describe the appearance and functions of the rugae in the stomach.
Ridges of muscle tissue called rugae line the stomach. The main function of the stomach involves. It produces an enzyme called pepsin which breaks down proteins into polypeptones which is a simpler version of proteins.
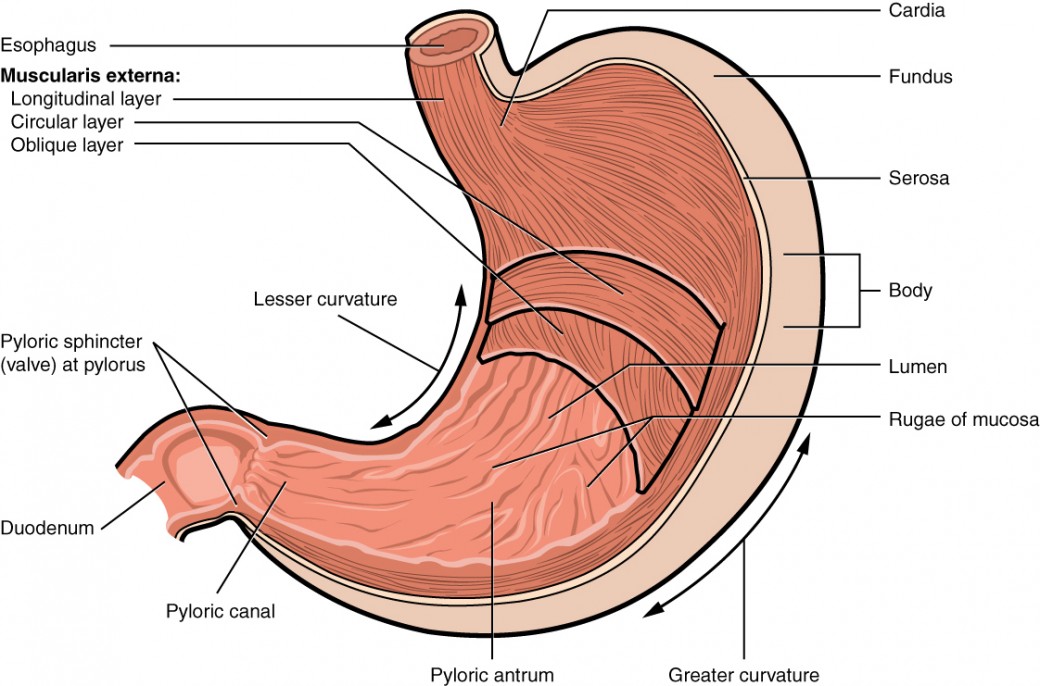
Stomach mucus protects the stomach from its own acid. Describe the basic histological tissue structure of the mucosa layer in the alimentary canal. The four main sections of the stomach are the cardia.
10 rows An important function of the stomach is to serve as a temporary holding chamber. Food acts as buffer so no inhibition of gastrin. B 1 U T.
Cells in the lining of your stomach secrete a strong acid and powerful enzymes that are responsible for the breakdown process. It is part of the digestive tract located between the esophagus and the duodenum. These enzymes continue the process of breaking down food into a usable form.
The stomach is a very complex organ. Anatomically it is divided into three regions the cardia corpus and antrum each with distinctive structures that promote specific functions. An important function of the stomach is to serve as a temporary holding chamber.
The stomachs main roles. Identify the unique features of the mucosa in the stomach and in the duodenum and explain how this uniqueness determines the function of the stomach and the duodenum. Ta o Words Question.
The main function of the stomach is to chemically and mechanically break down food. Anatomy and functions. The enzyme pepsin is responsible for protein breakdown.
Describe the appearance and function of the gall bladder. It is rounded and hollow and located near the diaphragm in the left part of your abdomen. The stomach consists of several important anatomical parts.
The stomach is a hollow organ or container that holds food while it is being mixed with stomach enzymes. The four key components of gastric digestive function are its function as a reservoir acid secretion enzyme secretion and its role in gastrointestinal motility. When food enters the mouth it is swallowed and enters the esophagus.
Food travels down the esophagus and enters the. Partial digestion of the food takes place here. The core function of the human stomach is as an aid to digestion.
Intestinal phase - chyme release inhibits gastrin release. You can ingest a meal far more quickly than it can be digested and absorbed by the small intestine. The stomach also produces digestive enzymes and hydrochloric acid that maintains the process of digestion.
The stomach muscles contract periodically churning food to enhance digestion. The stomach located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen is a J-shaped organ composed predominantly of involuntary smooth muscle. The stomachs main job is to store and digest the food and drink we take during our meals.
A bolus of food enters the stomach through the lower oesophageal sphincter which rapidly closes to prevent regurgitation of gastric secretions see part 1. Describe the appearance and function of the gall bladder. The stomach is J-shaped and it can expand to temporarily store food.
How does the gall bladder removal affect an individual. Stomach mucus might not be the first thing you consider when youre trying to be healthy. The cardia is located distal to the esophageal Z line where the.

Gastrointestinal Tract 2 The Structure And Function Of The Stomach Nursing Times
Comments
Post a Comment